When your IT policy requires a corporate proxy to scan and audit all outbound traffic the following options are available:
Some legacy corporate proxy configurations may be incompatible with the requirements of modern mobile architectures, such as the requirement of HTTP/2 requests from Apple to send push notifications to iOS devices.
In this case, a post-proxy relay (which accepts network traffic from a corporate proxy such as NGINX, and transmits it to the final destination) can be deployed to take messages from the Mattermost server passing through your corporate IT proxy in the incompatible format, e.g. HTTP/1.1, transform it to HTTP/2 and relay it to its final destination, either to the Apple Push Notification Service (APNS) and Google Fire Cloud Messaging (FCM) services.
The post-proxy relay can be configured using the Mattermost Push Proxy installation guide with connection restrictions to meet your custom security and compliance requirements.
You can also host in a trusted cloud environment such as AWS or Azure in place of a DMZ (this option may depend on your organization’s internal policies).
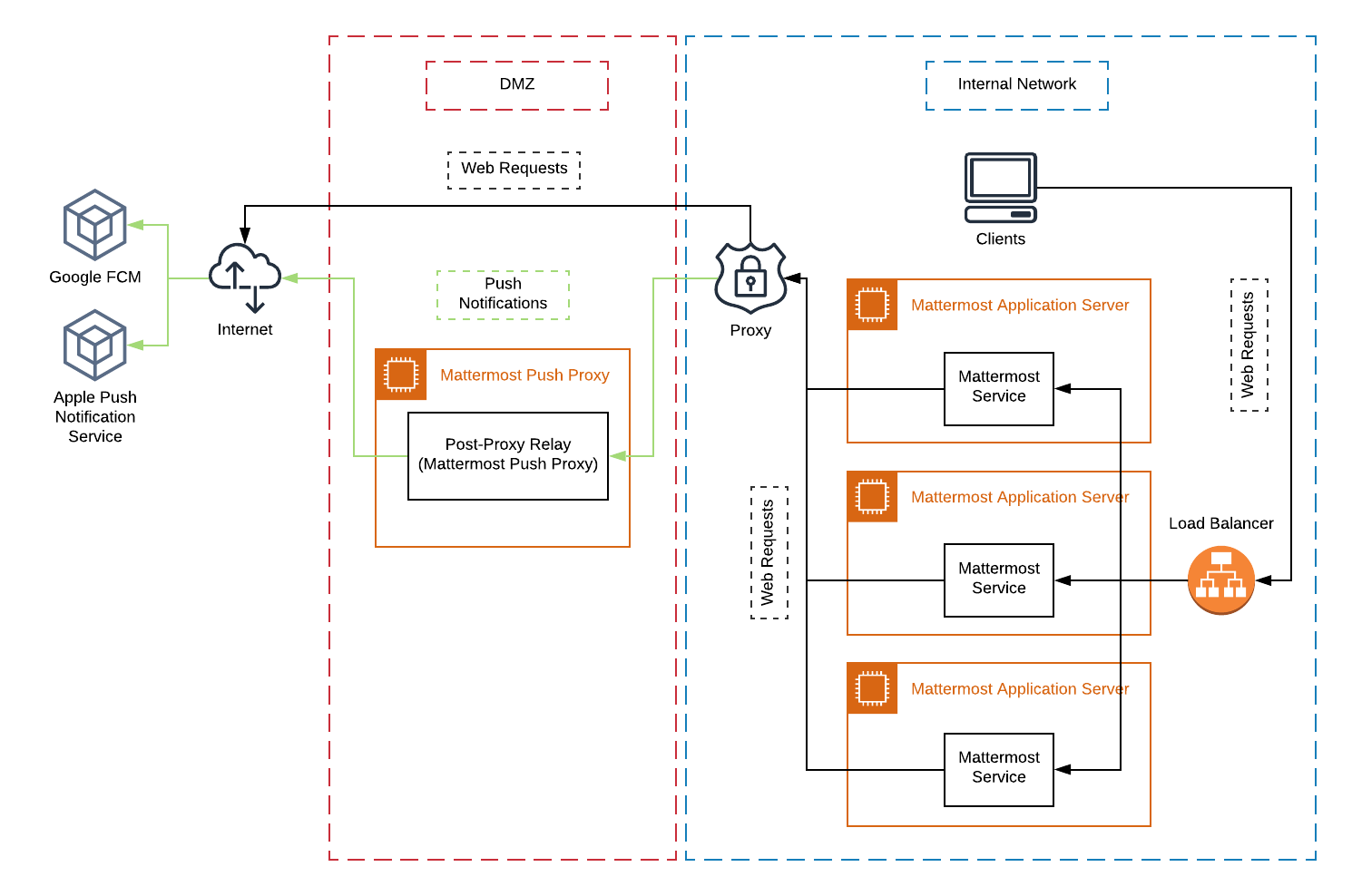
Depending on your internal IT policy and approved waivers/exceptions, you may choose to deploy the Mattermost Push Proxy to connect directly to Apple Push Notification Service (APNS) without your corporate proxy.
You will need to whitelist one subdomain and one port from Apple for this option:
api.development.push.apple.com:443api.push.apple.com:443You can use the mobile applications hosted by Mattermost in the Apple App Store or Google Play Store and connect with Mattermost Hosted Push Notification Service (HPNS) through your corporate proxy.
The use of hosted applications by Mattermost can be deployed with Enterprise Mobility Management solutions via AppConfig. Wrapping is not supported with this option.